Day 27
Assumptions for Linear Regression
EPSY 5261 : Introductory Statistical Methods
Learning Goals
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to …
- Check assumptions for a linear model.
Assumptions for a Linear Model
- L — Pattern is linear (plot your data)
- I — Observations are independent from each other (i.e., At a particular X value, one observation’s Y value does not affect observations’ Y values)
- N — The outcome variable is normally distributed
- Some also add “no outliers”
- E — Equal variance
- Variability in Y is constant at each X value (no fanning out of residuals on residual plot)
Linearity
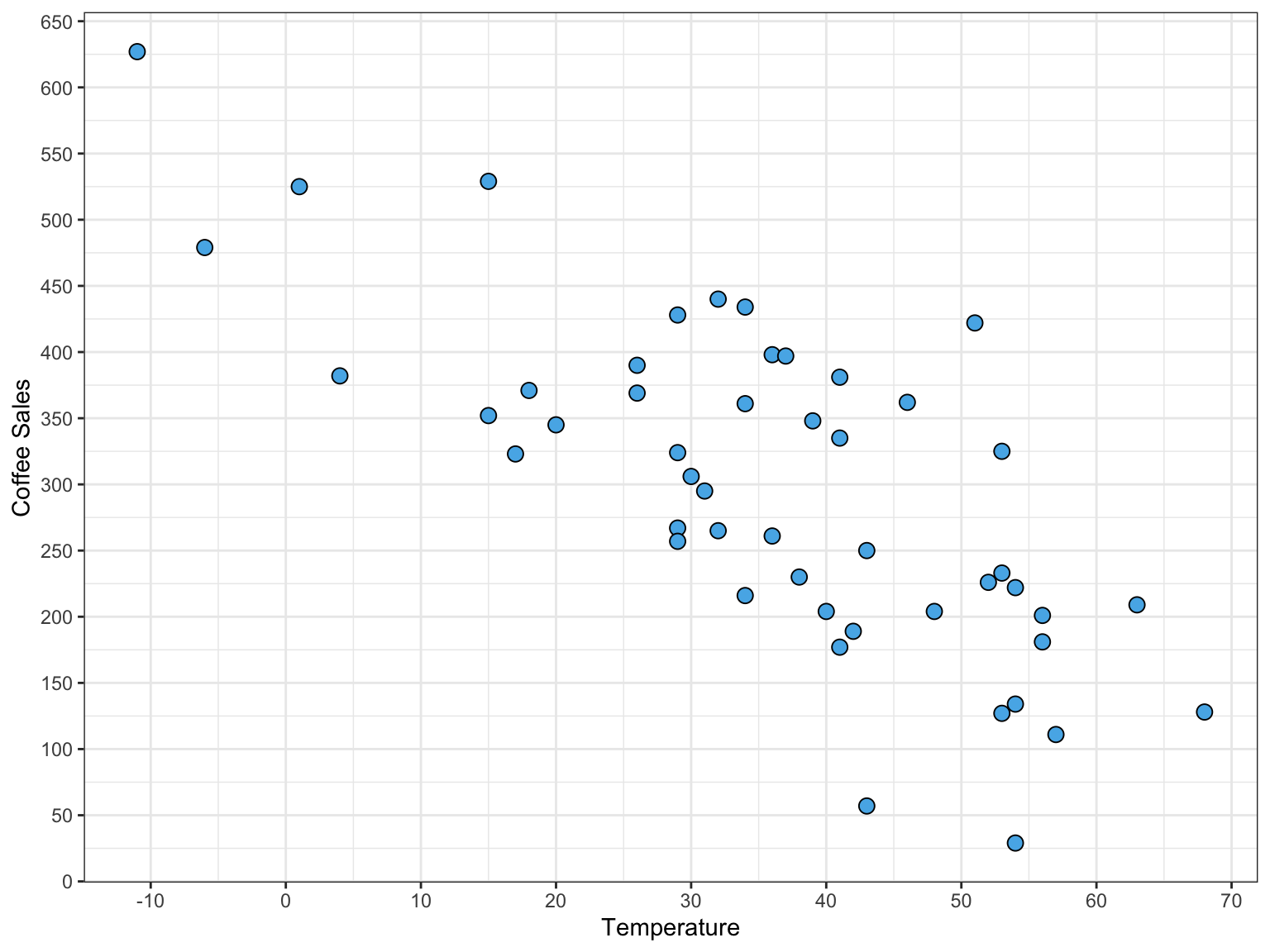
Independence
- Consider all the coffee sales at a particular temperature
- Reasonable to assume that one day’s coffee sales does not affect another day’s sales
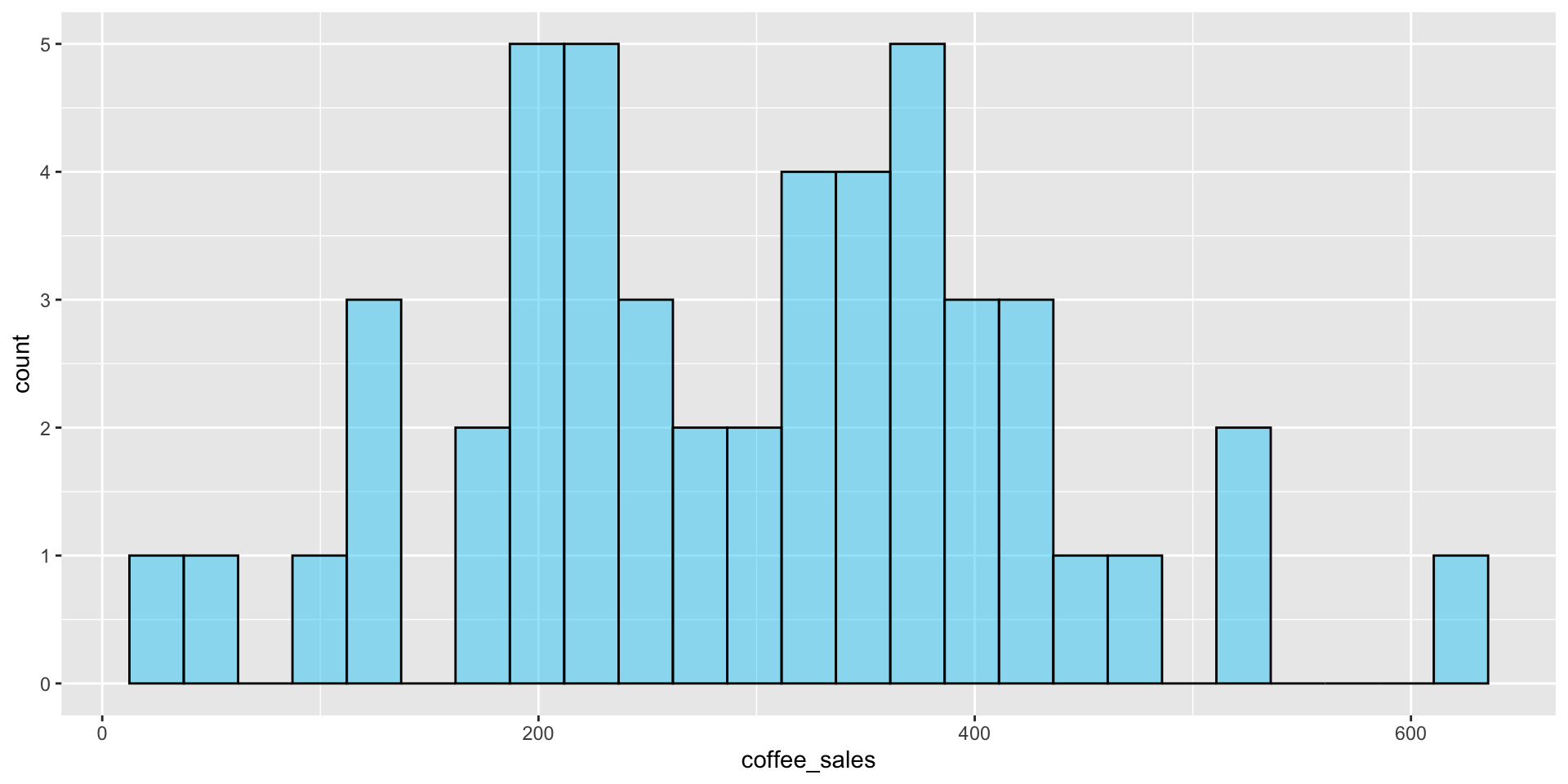
Normality
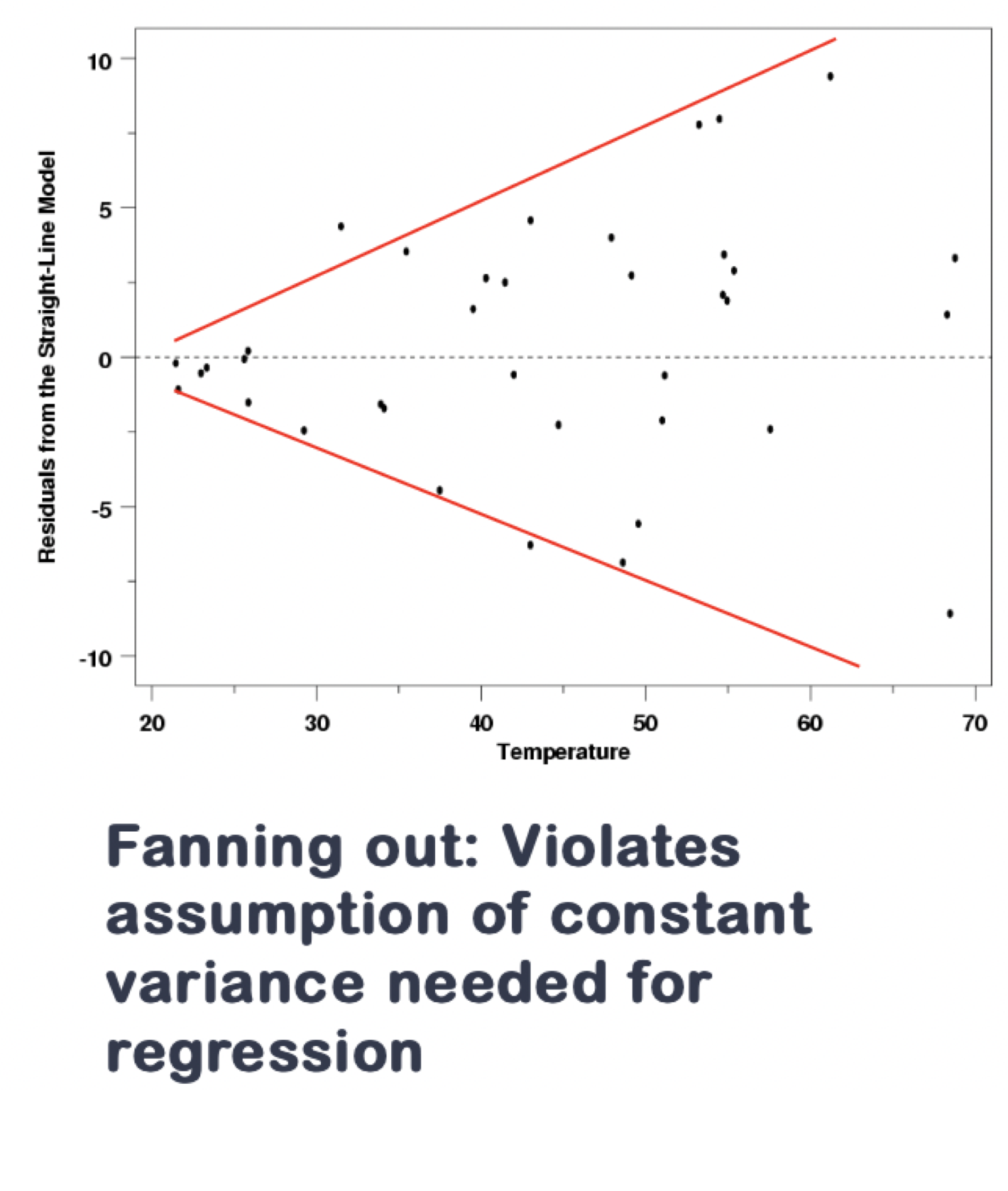
Equal Variance
- Should see that the range of residuals is constant (about the same) at each X value
A Residual Plot Showing Unequal Variance
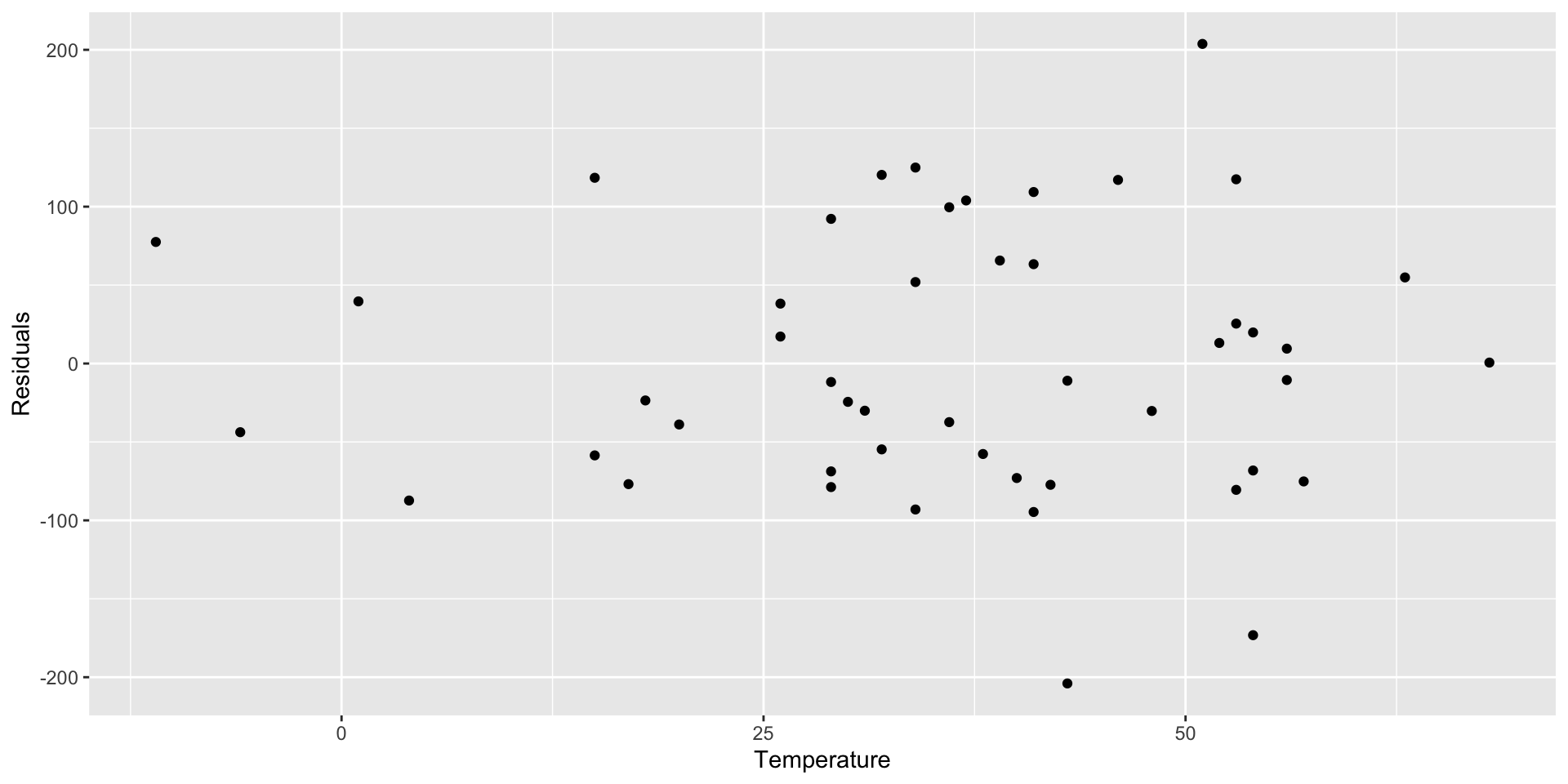
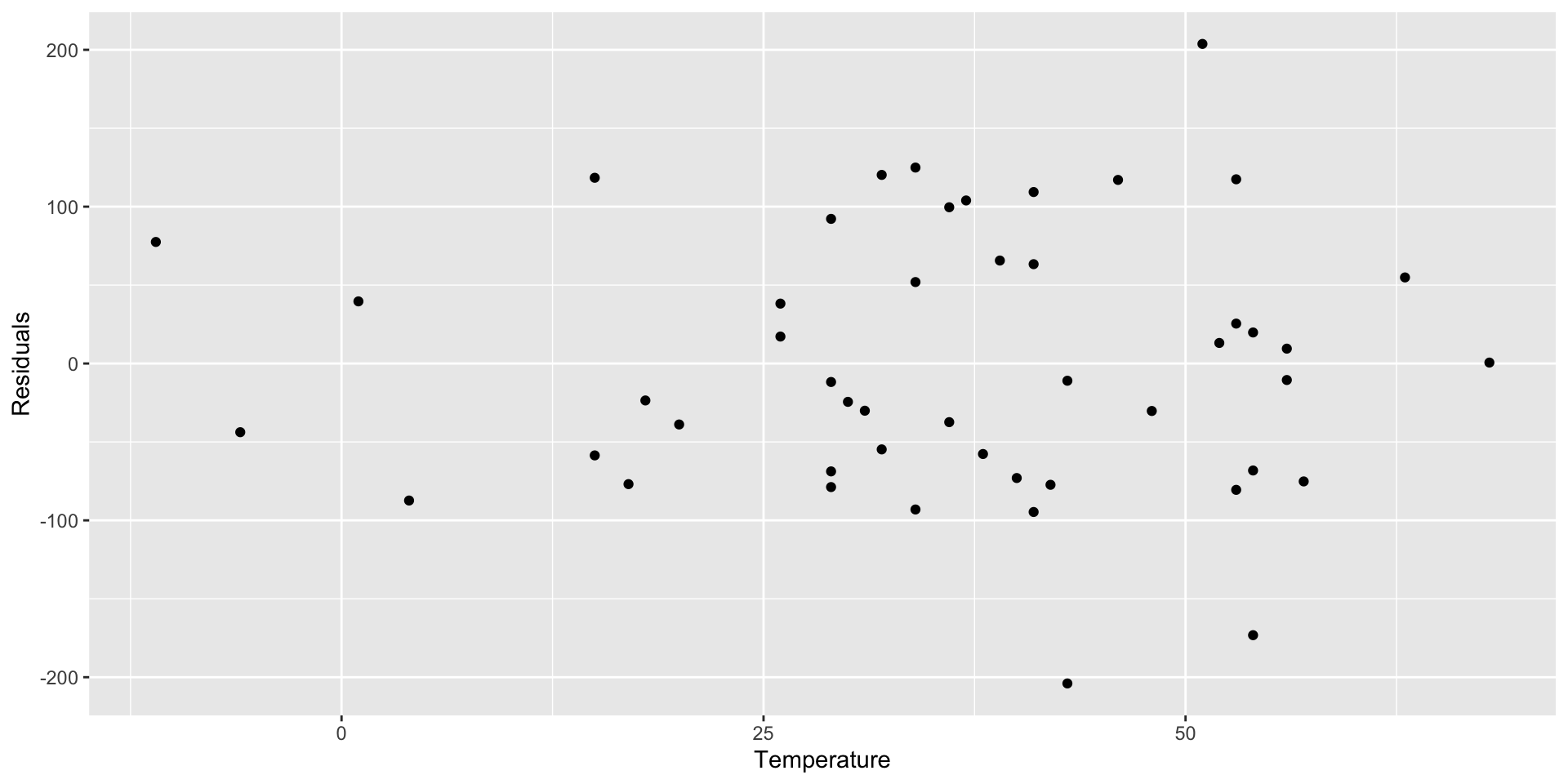
Residual Plot to Evaluate Linearity
- Random pattern around the line residual = 0
- Means your model is not systematically over or under-predicting
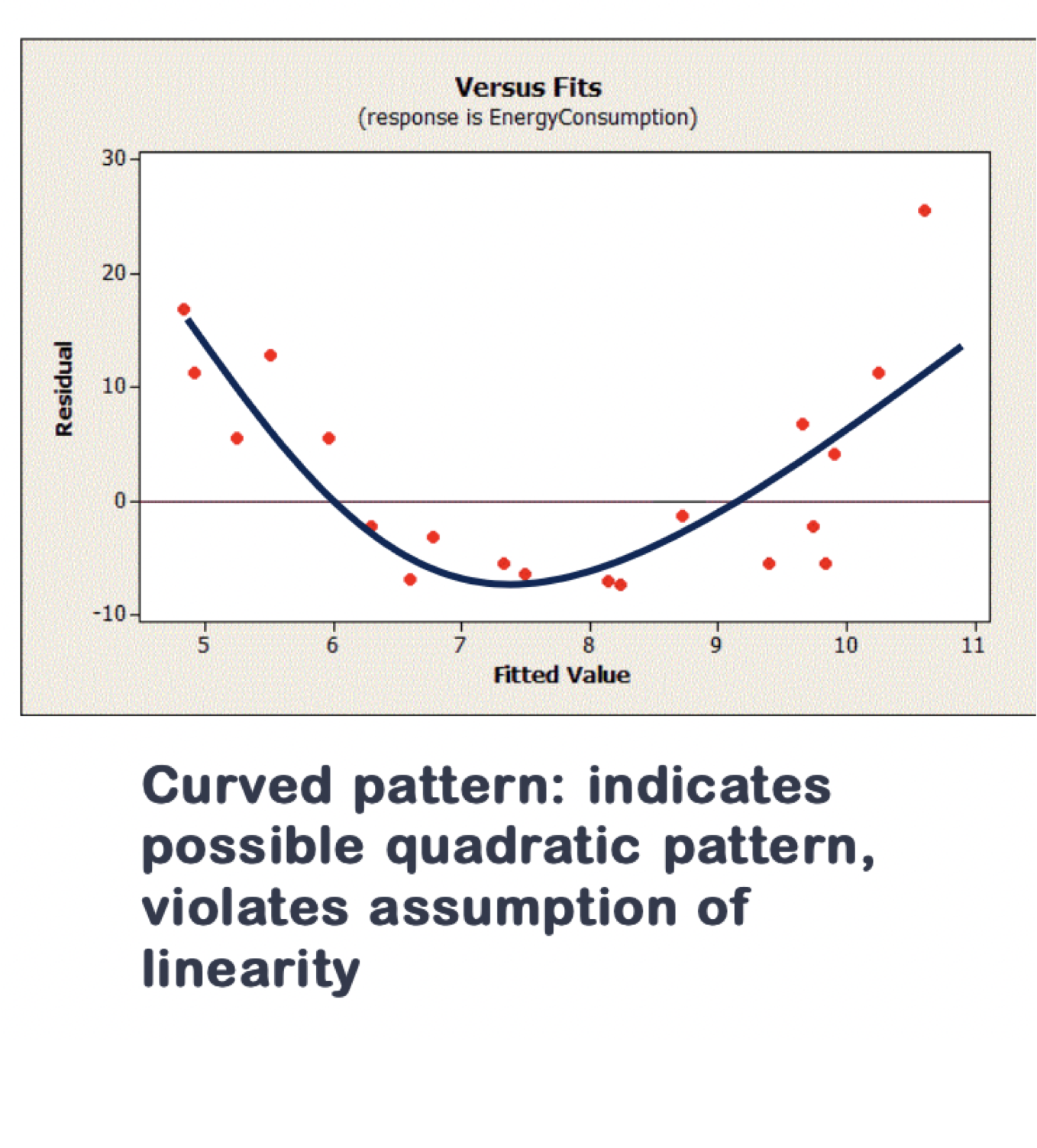
A Residual Plot Showing Non-linearity
Assumptions for Linear Regression Activity
Summary
- For hypothesis test results for regression to be valid, we need to meet the following assumptions:
- Linearity
- Independence
- Normality
- Equal variances
- The mnemonic LINE can be used to hep remember the assumptions.